 SHELLEY M. PAYNE
SHELLEY M. PAYNE
EDUCATION:
B.A. Rice University, 1972
Ph.D. Texas Health Science Center (Dallas), 1977
POSTDOC: University of California at Berkeley
RESEARCH INTERESTS:
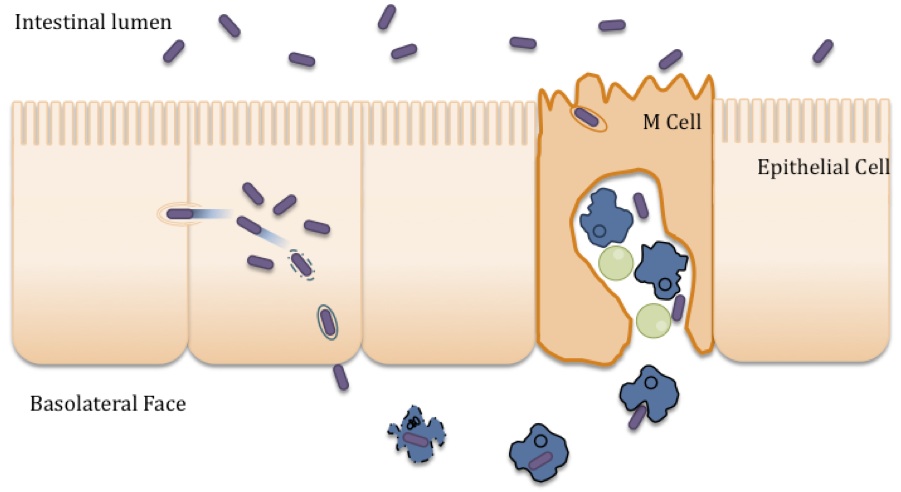
Our studies focus on the genetics and regulation of iron acquisition
systems and other virulence factors of Shigella and Vibrio species. The iron transport
systems are of interest because the ability of potential pathogens to acquire iron from
the host is an important determinant of microbial virulence. Iron is required for growth
of bacteria, but little free iron is available in mammalian hosts. Many bacteria have been
found to secrete high affinity iron-binding compounds, or siderophores, which may function
to remove iron from host proteins and make it available to the microorganism for growth in
vivo.
Vibrio species produce a variety of siderophores and iron-regulated outer membrane
proteins. In response to iron deprivation, Vibrio cholerae synthesizes a norspermadine
containing siderophore, and five cell surface proteins, including receptors for the
siderophore and for heme. The Shigella species, a group of enteric pathogens, have at
least three distinct iron transport systems. Two of these, the aerobactin and enterobactin
systems, consist of siderophores and their associated outer membrane receptor proteins.
Expression of these systems is regulated at the level of transcription by the
concentration of iron within the cell. A third pathway is required for the transport and
utilization of iron in the form of heme. Virulence assays of mutants defective in one or
more of these systems suggest that siderophores provide iron in the extracellular
environment while heme transport is utilized by Shigella growing intracellularly within
epithelial cells. A heme-binding protein is found on the surface of wild-type Shigellae.
Although this protein is not required for heme transport, it is required for invasion of
intestinal epithelial cells by S. flexneri. The protein allows the bacteria to bind large
amounts of heme on the surface of the bacteria and promotes the attachment of the bacteria
to the host cells. This protein is encoded on a large 220 kilobase plasmid, and its
synthesis is regulated by both temperature and pH. Analysis of regulatory mutants
indicates that at least two loci, one chromosomal and one plasmid encoded, are responsible
for the regulation of the structural gene for this cell surface protein. Genetic and
recombinant DNA techniques are being used to characterize chromosomal and plasmid
sequences involved in iron transport and invasion in these enteric pathogens. The genes
have been cloned and gene fusions have been constructed to measure the expression of these
genes under different environmental conditions. Techniques have been developed also to
measure gene expression and synthesis of virulence-associated proteins by S. flexneri
growing within host cells. These studies will allow us to determine the molecular
mechanisms of iron acquisition and ultimately to assess the roles of these systems in
bacterial infections.
SELECTED PUBLICATIONS (clicking on the citation will take you to the abstract for the manuscript):
Mey AR, Craig SA, Payne SM. (2005) Characterization of Vibrio cholerae RyhB: the RyhB regulon and role of ryhB in biofilm formation. Infect. Immun. 73(9): 5706-5719. (Abstract)
Wyckoff EE, Lopreato GF, Tipton KA, Payne SM. (2005) Shigella dysenteriae ShuS promotes utilization of heme as an iron source and protects against heme toxicity. J. Bacteriol. 187(16): 5658-5664. (Abstract)
Wyckoff EE, Schmitt M, Wilks A, Payne SM. (2004) HutZ is required for efficient heme utilization in Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 186(13):4142-4151.(Abstract)
Wei J, Goldberg MB, Burland V, Venkatesan MM, Deng W, Fournier G, Mayhew GF, Plunkett III G, Rose DJ, Darling A, Mau B, Perna NT, Payne SM, Runyen-Janecky LJ, Zhou S, Schwartz DC, Blattner FR.(2003).
Complete Genome Sequence and Comparative Genomics of Shigella flexneri Serotype 2a Strain 2457T. Infect. Immun.71(5):2775-2786. (Abstract)
Runyen-Janecky LJ, Reeves SA, Gonzales EG, Payne SM.(2003). Contribution of the Shigella flexneri Sit, Iuc, and Feo Iron Acquisition Systems to Iron Acquisition In Vitro and in Cultured Cells. Immun. 71(4):1919-28. (Abstract)
Mey AR and Payne SM. 2003. Analysis of residues determining specificity of Vibrio cholerae TonB1 for its receptors. Journal of Bacteriology. 185: 1195-207. (Abstract)
Purdy GE, Hong M, Payne SM. 2002. Shigella flexneri DegP facilitates IcsA surface expression and is required for efficient intercellular spread. Infect. Immun. 70:6355-64. (Abstract)
Runyen-Janecky LJ, Payne SM. (2002). Identification of chromosomal Shigella flexneri genes induced by the eukaryotic intracellular environment. Infect. Immun. 70(8):4379-88. (Abstract)
Mey AR, Wyckoff EE, Oglesby AG, Rab E, Taylor RK, Payne SM. 2002.
Identification of the Vibrio cholerae Enterobactin Receptors VctA and
IrgA: IrgA Is Not Required for Virulence. Infect. Immun. 70:3419-3426. (Abstract)
Mey, A.R. and S.M. Payne. 2001. Haem utilization in Vibrio cholerae involves multiple TonB-dependent haem receptors. 42: 835-849. (Abstract)
Torres AG, Redford P, Welch RA,
Payne SM. 2001. TonB-dependent systems of uropathogenic Escherichia coli:
aerobactin and heme transport and TonB are required for virulence in the
mouse. Infect. Immun. 69(10):6179-85 (Abstract).
Purdy, G.E. and S.M. Payne. 2001. The SHI-3 Iron Transport Island of Shigella
boydii 0-1392 Carries the Genes for Aerobactin Synthesis and Transport. J.
Bacteriol. 183:4176-4182. (Abstract)
Wyckoff,
S.S. Seliger, A.R. Mey, A.-M. Valle and S.M. Payne. 2001. The two TonB systems of Vibrio cholerae: redundant and specific functions. Mol. Microbiol. 39: 801-812. (Abstract)
Reeves, S.A.,
Wyckoff, E.E., A. M. Valle, S. L. Smith, and S. M. Payne. 1999. A multifunctional ATP-binding cassette transporter system from Vibrio cholerae transports vibriobactin and enterobactin. Journal of Bacteriology 181(24):7588-96. (Abstract)
Vokes, S.A., S.A. Reeves, A.G. Torres, and S.M. Payne. 1999. The aerobactin iron transport system genes in Shigella flexneri are present within a pathogenicity island. Molecular Microbiology 33(1):63-73. (Abstract).
Runyen-Janecky, L.J., Hong, M., Payne, S.M. 1999. Runyen-Janecky, L.J., Hong, M., Payne, S.M. 1999. The virulence plasmid-encoded impCAB operon enhances survival and induced mutagenesis in Shigella flexneri after exposure to UV radiation. Infection and Immunity 67(3):1415-23. (Abstract)
Hong, M., Gleason, Y., Wyckoff, E.E. and S.M. Payne. 1998. Identification of Two Shigella flexneri Chromosomal Loci Involved in Intercellular Spreading. Infection and Immunity. 66(10):4700-4710.(Abstract)
Occhino, D.A., Wyckoff, E.E., Henderson, D.P., Wrona, T.J., and S.M. Payne. 1998.Vibrio cholerae Iron Transport: Haem Transport Genes are Linked to One of Two Sets of tonB, exbB, exbD Genes. Molecular Microbiology. 29(6):1493-1507.(Abstract)
Wyckoff, E.E., Duncan, D., Torres, A.G., Mills, M., Maase, K. and S.M. Payne, 1998. Structure of the Shigella dysenteriae haem transport locus and its phylogenetic distribution in enteric bacteria. Molecular Microbiology. 28(6):1139-1152.(Abstract)
Wyckoff, E.E., Stoebner, J.A, Reed, K.E., and S. M. Payne. 1997. Cloning of a Vibrio cholerae vibriobactin gene cluster: Identification of genes required for early steps in siderophore biosynthesis. Journal of Bacteriology. 179(22):7055-7062.(Abstract)
Mills, M., and Payne, S.M. 1997. Identification of shuA, the gene encoding the heme receptor of Shigella dysenteriae, and analysis of invasion and intracellular multiplication of a shuA mutant. Infection and Immunity. 65(12):5358-5363.(Abstract)
Hong, M. and Payne, S.M. 1997. Effect of mutations in Shigella flexneri chromosomal and plasmid-encoded lipopolysaccharide genes on invasion and serum resistance. Molecular Microbiology. 24(4):779-91.(Abstract)
Torres, A.G. and Payne, S.M . 1997. Haem iron-transport system in enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Molecular Microbiology. 23(4):825-33.(Abstract)
Headley, V., Hong, M., Galko, M., and Payne, S.M . 1997. Expression of aerobactin genes by Shigella flexneri during extracellular and intracellular growth. Infection & Immunity. 65(2):818-21.(Abstract)
Pope, L.M., Reed K.E., and Payne, S.M. 1995.Increased protein secretion and adherence to HeLa cells by Shigella spp. following growth in the presence of bile salts. Infection & Immunity. 63(9):3642-8.(Abstract)
Mills, M., and Payne, S.M. 1995. Genetics and regulation of heme iron transport in Shigella dysenteriae and detection of an analogous system in Escherichia coli O157:H7. Journal of Bacteriology. 177(11):3004-9.(Abstract)
Henderson, D.P., and Payne, S.M. 1994. Vibrio cholerae iron transport systems: roles of heme and siderophore iron transport in virulence and identification of a gene associated with multiple iron transport systems. Infection & Immunity. 62(11):5120-5.(Abstract)
Payne, S.M. 1994. Detection, isolation, and characterization of siderophores. Methods in Enzymology. 235:329-44.
Henderson, D.P., and Payne, S.M. 1994. Characterization of the Vibrio cholerae outer membrane heme transport protein HutA: sequence of the gene, regulation of expression, and homology to the family of TonB-dependent proteins. Journal of Bacteriology. 176(11):3269-77. (Abstract)
Payne, S.M. 1993. Iron acquisition in microbial pathogenesis. Trends in Microbiology. 1(2):66-9.
Henderson, D.P. and Payne, S.M. 1993. Cloning and characterization of the Vibrio cholerae genes encoding the utilization of iron from haemin and haemoglobin. Molecular Microbiology. 7(3):461-9.(Abstract)
Stoebner, J. A., J. R. Butterton, S. B. Calderwood, and S. M. Payne. 1992. Identification of the vibriobactin receptor of Vibrio cholerae. Journal of Bacteriology. 174: 3270-3274(Abstract).
EMAIL ADDRESS: payne@mail.utexas.edu
PERSONAL WEB PAGE:

