|
(click
on the main point headings to jump to the selected
location in the notes)
Importance
of spores
Biological:
a.
Insure survival because of dormancy
qualities
b.
Allow for dissemination of fungus to new
substrates
c.
Allow for reproductive multiplication of the
hyphal fungus
d. Allow for
the establishment of new individuals with
genetic potentials different than parents
Practical:
a.
Allow for "rapid" identification
b. Sources of
infection of plants, animals, etc.
c.
Sources of contamination
88
(Back
to main points)
Fungal
spore types
1.
Endogenous mitospores* -zoospores and
sporangiospores of fungal-like protists and
zygomycota
2.
Exogenous mitospores* - conidia,
blastospores, teliospores**, etc. of
ascomycota, basidiomycota, z
fungi imperfecti
3.
Endogenous meiospores+
-ascospores of ascomycota
4.
Exogenous meiospores+
-basidiospores of basidiomycota
5.
Karyospores+
- zygospores, oospores, resting spores and
resting sporangia of zygomycota, oomycota & chytridiomycota
respectively
6.
Chlamydospores* - vegetative units
that attain spore-like characteristics
(dormancy qualities).
*
asexual
+
sexual
**
N+N
89
(Back
to main points)
Generalized
fungal life cycle
1.
Period of vegetative growth
(colonization and substrate exploitation)
2.
Period of asexual reproduction (often
called anamorphic* phase of fungal life
cycle)
3.
Period of sexual reproduction (often
called the teleomorphic phase of fungal life
cycle)
*
Often the most common name of a fungus is
its anamorphic name (because discovered
and/or observed first)
90
(Back
to main points)
Taxonomic
systems for identification of the anamorphs
of conidiogenous fungi
1.
The
Saccardo System ~ 1880s
identification based totally on final
morphology of conidium
2.
*Vuillemin
~ 1910
concept
of thallospores & conidia
3.
The
Hughes-Tubaki-Barron system ~1968+
based primarily on mechanism of conidium
development
4.
Ellis
(Cole, Kendrick & Sampson)_Systems
~1971+
based on both mechanisms of conidium &
conidiophore development (mod. of #3)
98
(Back
to main points)
Types
of conidia
Thallic
= conidia produced by the conversion of a
pre-existing hypha, which may or may not
freely disarticulate
Blastic
= conidia which are produced by blastic
outgrowth that is similar to yeast budding.
8-2/99
(Back
to main points)
Conidial
types per Hughes-Tubacki-Barron and per
Ellis
Thallic
conidia
Holothallic
1.
Aleuroconidia
Holoarthric
and enteroarthric
2.
Arthroconidia
Blastic
conidia
Holoblastic
3.
Blastoconidia
4.
Botryoblastoconidia
5.
Poroconidia
6.
Sympoduloconidia
Enteroblastic
7.
Phialoconidia
8.
Annelloconidia
101
(Back
to main points)
Thallic
conidia
1.
Arthroconidia
2.
Meristem arthroconidia
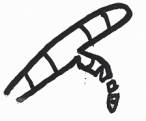
Geotrichum
Oidiodendren
random
separation
basipitalous formation
3.
Aleurioconidia (Holothallic)

Microsporum
8-10/111
(Back
to main points)
Blastic
conidia
4.
Annelloconidia
|
Annellations
(annellidic)
Basipetalous
&
(Enteroblastic)
|
 Scopulariopsis
Exophiala
|
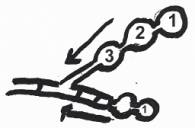
5.
Blastoconidium
|
Cladosporium |
 |
Acropetalous
6.
Botryoblastoconidia
 |
Oedocephalum
Sometimes produce
secondary
acropetalus
conidia
(Holoblastic)
|
Superficially
looks like Aspergillus
8-11/112
(Back
to main points)
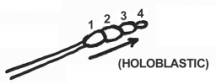
7.
Poroconidia
Helminthosporium
(Holoblastic)
8.
Sympoduloconidium

Fusicladium
(Holoblastic)
9.
Phialoconidia
produced
enteroblastically from phialids
Penicillium


Aspergillus
Phialophora
(Phialidic)
8-12/113
(Back
to main points)
|

