Isolation, Identification, and Analysis of a cDNA encoding an Annexin-like Protein from Arabidopsis thaliana
Amish M. Dave, Arthur Dandrea, Oliver Lou, and K. Sathasivan*
Department of Biology, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX 78712
Key Words: annexin I, Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
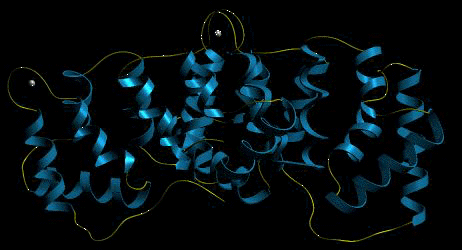
Annexins are a family of calcium requiring proteins that display a high binding affinity for phospholipids. We obtained and sequenced a cDNA clone from A. thaliana and identified it as coding for a novel annexin-like protein. Using computer and database analysis, we were able to identify our cDNA insert as an annexin-like gene with high certainty, and compared its amino acid sequence homology to other well characterized annexin proteins. The deduced protein sequence of our novel annexin-like cDNA showed homology with the respective sequences of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum, 69%), chili pepper (Capsicum annuum, 62%), corn (Zea mays, 60%), and human (24%) annexin proteins. Protein motif searches revealed a variety of phosphorylation sites, while protein secondary structure predictions showed annexin to be largely alpha-helical. Southern hybridization experiments using a complete annexin cDNA as a probe revealed a small annexin gene family in. Northern hybridization studies using the same probe showed the complete annexin mRNA to be expressed only in the flower of the A. thaliana, and an increased annexin mRNA transcription in wounded plants. These results indicate that the expression of the annexin-like protein could be tissue-specific, and possibly involved in plant defense mechanisms. Further implications of our results with regard to the role of annexin in A. thaliana are also presented.
 Continue..........
Continue..........
 Some Molecular Biology Links
Some Molecular Biology Links
 Contact Authors:
Contact Authors:
![]() Continue..........
Continue..........![]() Some Molecular Biology Links
Some Molecular Biology Links
 Contact Authors:
Contact Authors: