Polygenic Traits
Mendel’s crosses for plant height vs. human height.
The problem with the comparison is that a single gene pair is in control of height in pea plants, whereas several gene pairs determine human heights.
The gene product in plants that controls height is gibberellin
Short plants have a mutation in this gene
Traits that are determined by two or more genes are referred to as polygenic traits
Human height exhibits continuous variation

Pea plant height shows discontinuous variation (tall or short)
Multifactorial Traits
Traits that result from the interaction of one or more environmental factors and two or more genes.
Ex
Japanese soldiers during WWII
Old diet was higher in carbs and in comparison to today were on average 3 inches shorter.
Suggesting some kind of environmental influence on a person’s phenotype.
Ex Obesity
Studies have looked at both identical twin and non identical twin and found a strong genetic correlation to obesity.
Pina Indians
Evidence supports the contention that they may possess a “fat gene”
May have been favored in people when food supply was scarce.
But:
OB/OB Mouse Model

Down Syndrome
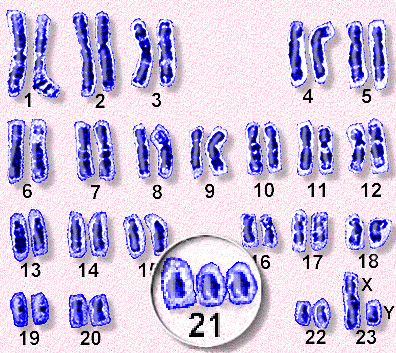
Karyotype
the appearance of the chromosomal makeup of a somatic cell in an individual or species (including the number and arrangement and size and structure of the chromosomes)
2n + 1 (chromosome 21)
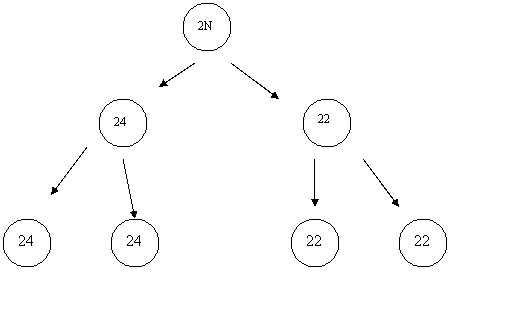
2N + 1 2N – 1
Most fetuses that have an abnormal chromosome number are aborted
3 Ways to get Down Syndrome
The normal status of the chromosomes is two pairs of 23 types of autosomal chromosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes. 46XX is female euploidy, 46XY is male euploidy.
v Where the chromosomes are either
1. haploid (23)
2. Diploid (46)
3. Triploid (67)
v Anuploid
i. Abnormal chromosome number (too few or too many)
1. Monosomy (2N-1)
2. Trisomy (2N+1)
Q. Why couldn’t a tetraploid situation occur in humans? (4N)
Q. What was one possible explanation as to why chromosomes become sticky?
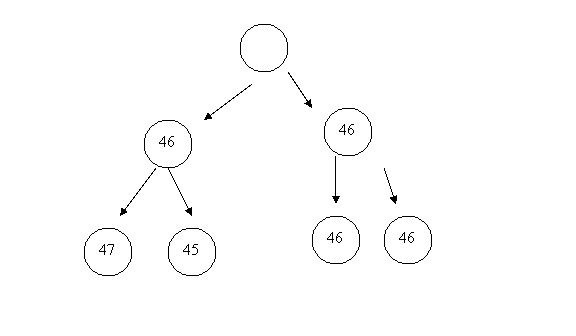
Accounts for approx 7% of all D.S. cases
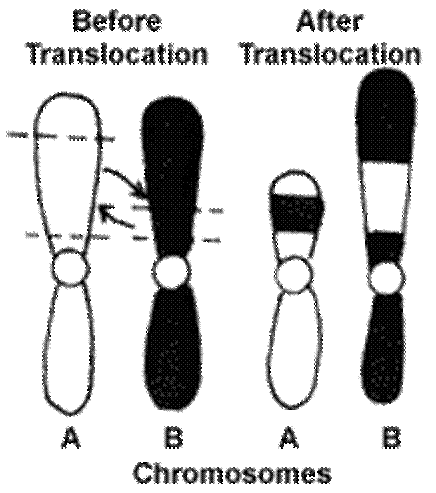
|
|
Chances of Downs