Agglutination
· This is the interaction between Ab and a particular Ag, that results in physical clumping.
· This clumping is agglutination
· Agglutination rxns depend on X-linking of polyvalent antigens.
Clinical uses for MC Ab’s

Problems with monoclonal therapy
Recap
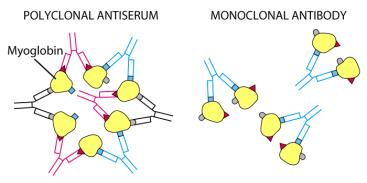
Monoclonal Ab recognize one epitope
Polyclonal Ab recognize many epitopes (eg insulin)
Affinity = strength of interactions between single epitope on an Ag and a single binding site on an Ab
Avidity = Avidity is a measure of the overall strength of binding of an antigen with many antigenic determinants and antibodies

Precipitation Expts
· Antibodies and Ag form lattice structures that will develop into visible precipitate.
· Formation of Ab-Ag lattice depends on
1. Ab must be bivalent ( a precipitant will not form with fab fragments)
2. Ag must be bivalent or polyvalent: that is it must have at least 2 copies of the same epitope or have different epitopes that will react with different Ab in a polyclonal antisera
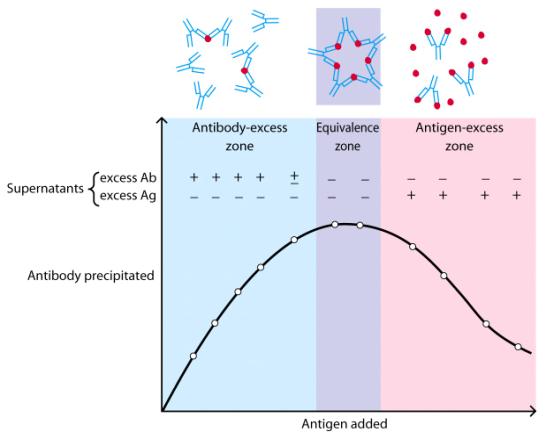
Factors affecting precipitation:
· Levels of Ab and Ag
·
Immunodiffusion
Immune precipitates can also form on and agar matrix
· A ring of precipitation will occur in the zone of equivalence
· No visible ring will form in the zone of excess.
2 Types of Immunodiffusion:
1. Radial
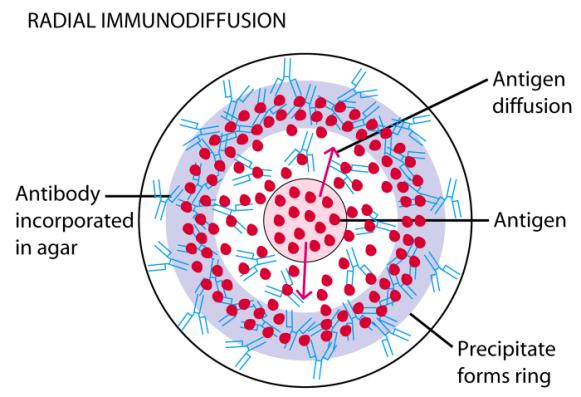
· As Ag diffuses into agar, precipitant ring will form at optimal Ab-Ag concentrations
· Comparing the area of the ring with that of a standard sample of known Ag concentration, the test sample's Ag concentration can therefore be determined.
2. Double Immune Diffusion
·
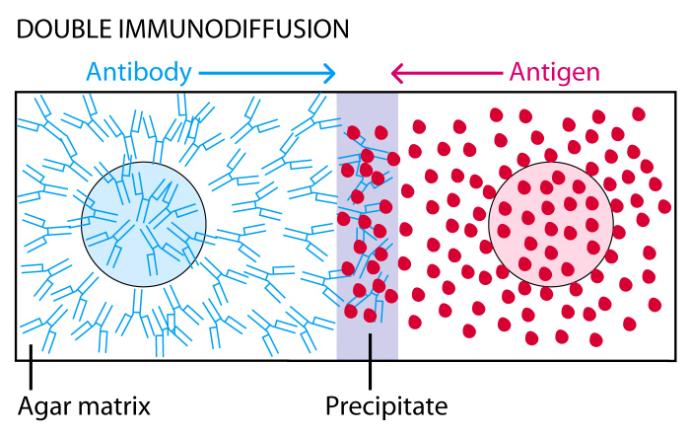
· Both Ab and Ag diffuse radially from the wells
· As equivalence is reached a visible ring of precipitation is formed
Advantages of these types of assays
Cheap
Reliable
Repeatable
Automated
Real life examples of these tests
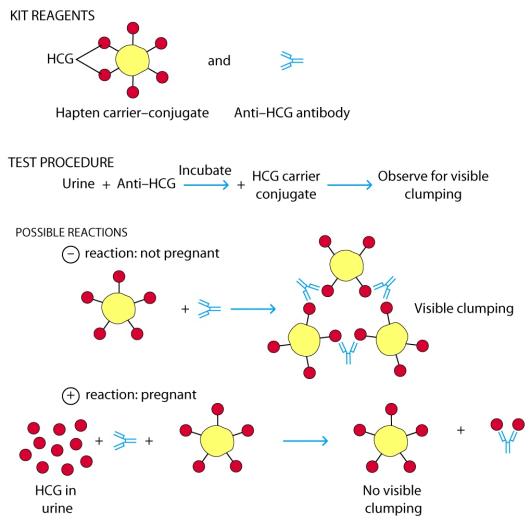
Home Pregnancy Test
· It is a modification of an agglutination experiment
· Called agglutination inhibition
· Good because it is sensitive to small amounts of Ag
· Based on competition
Radioimmune Assay
1000 times more sensitive than agglutination
Concept
Principle of RIA involves competitive binding of radiolabeled Ag and unlabeled Ag to a high affinity Ab
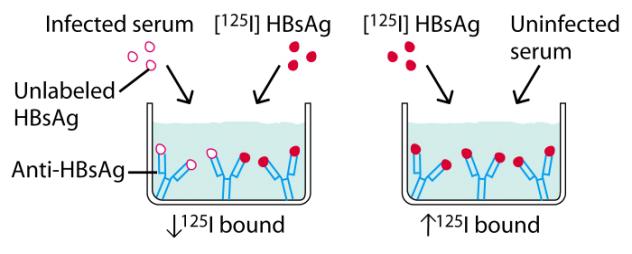
· The increase in the concentration of the Ag in the unlabeled test sample, the more radiolabeled Ag will be displaced from the Ag binding sites
· Therefore the concentration of the test sample Ag is a measure of the decrease in the amount of radiolabeled Ag bound to the Ab
Immunofluorescence
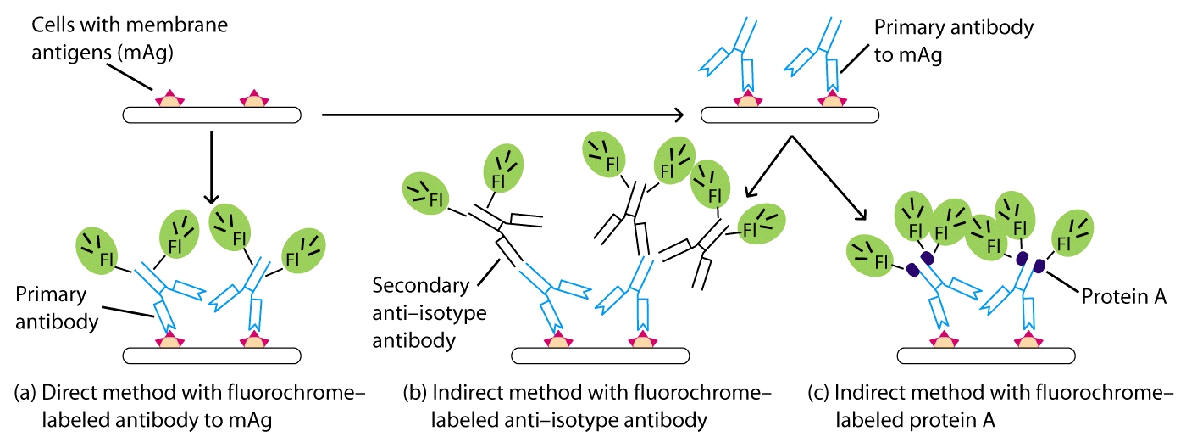
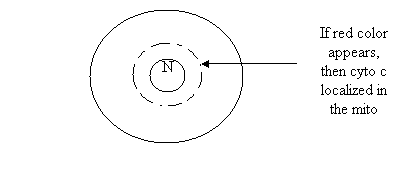
You are trying to determine that the mitochondrial protein cytochrome C is localized in the mitochondria
Use and Ab (red label) that is specific to cyto C
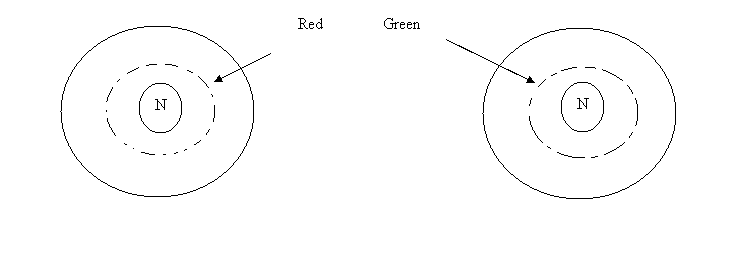
Ex
You are trying to determine if cytochrome c and caspase 9 are localized in the mitochondria
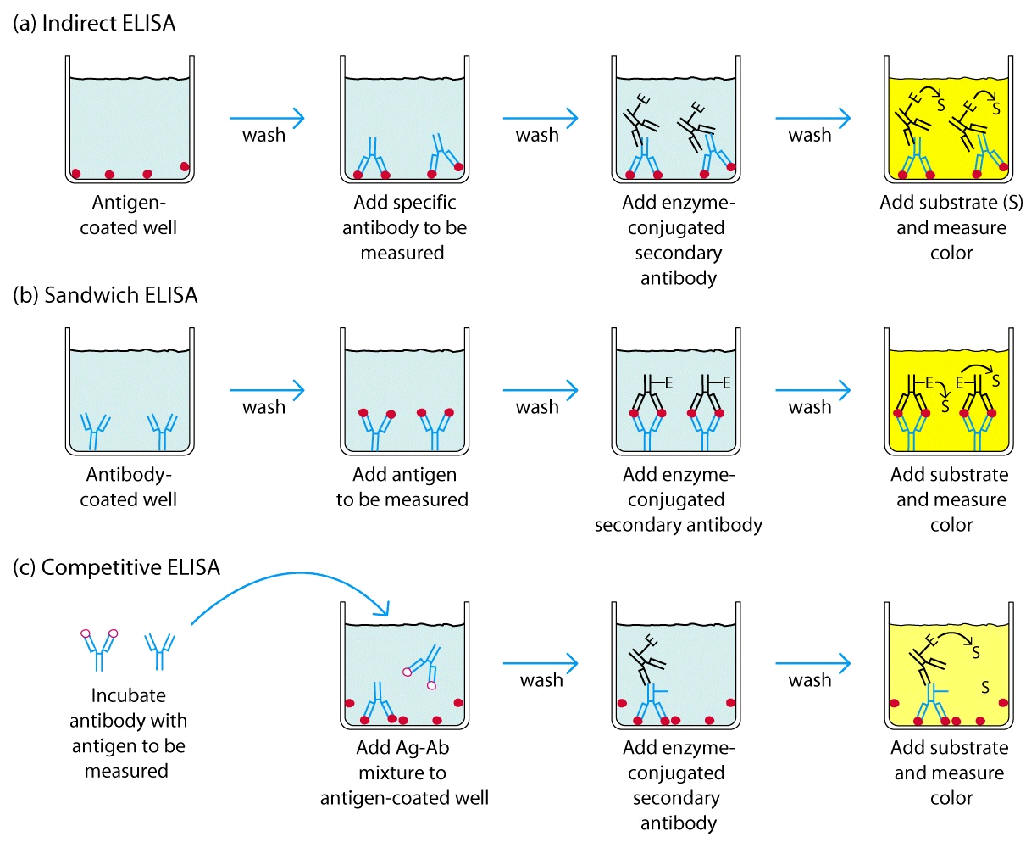
ELISA
Concept
Such enzymes include:
Advantages of the Elisa are that they are safer and cheaper.
Sensitive, reliable, automated, easy to quantitate.
Common uses
HIV testing (initial test)
Drug testing (workplace, athletic events)
Q. What do you think the limitations of the ELISA would be regarding HIV presence/absence?
Reasons for labeling the secondary Ab
Direct ELISA
Indirect ELISA - Ab detection
This is the method of choice to detect the presence of serum Ab against HIV.
Sandwich Elisa - Ag detection
Radiolabeled Ab used before ELISA
Problems:
Research Applications
If you were to ask the question.......
Does a patient express Class II MHC?....1st choice would be FACS
If patient is expressing Class II MHC then you would see equal amounts of green and red.
If you were to ask the question..............
Are the α and β chains the correct size? (28 and 33 kD)
You could use a radiolabeled membrane protein. (125I)
Beads act to trap the primary Ab
The purified sample to Ag-Ab complex can then be run on Western Blot to see the size of the fragments
Western blotting
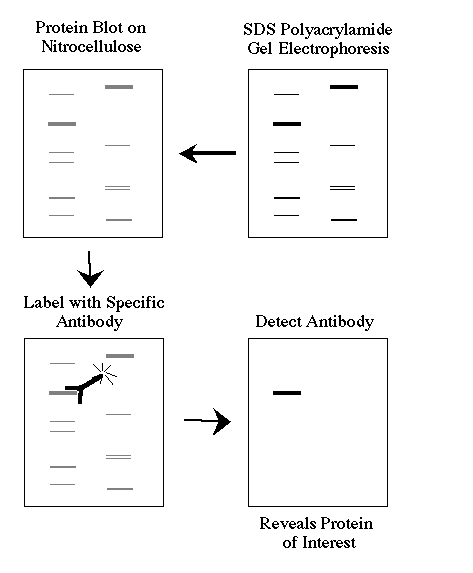
Western Blotting allows you to determine the molecular weight of the protein of interest.
Other uses for Westerns
Parp cleavage - detection of apoptosis
Enhanced Chemiluminescence
The ECL system is probably the most sensitive western detection system currently available.
Protein
F
Gives off light that can be exposed to film
Chemical used is Luminol

Oxidation of the compound Luminol by H2O2 and the enzyme HRP produces light.
Main advantages over chromogenic assays is the enhanced sensitivity.
Disadvantages
Labor intensive
Not setup for mass production
Applications
Tumor Cells in peripheral blood/tissues
If you are looking for a tumor cell within a population of normal cells, you could make and Ab specific for the tumor cell in question
ex 66-cl-4 GFP cells
Localization assays
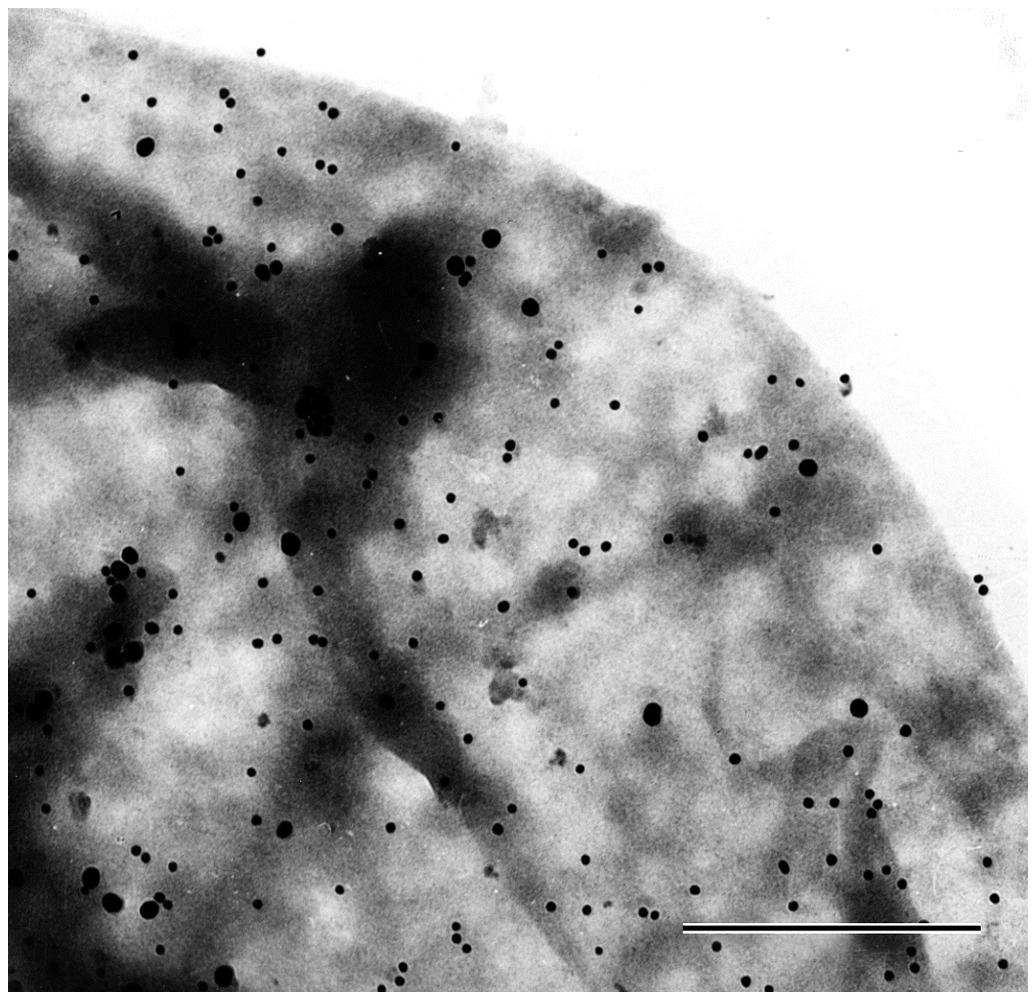
Immunoelectron Microscopy
In this technique an electron dense label can be directly conjugated to the Fc region of a specific Ab for direct staining.
Because the electron dense label absorbs electrons, it can be viewed with an EM as small black dots
Ex
Q. Do B cells in question express Class I and II?
Use an Ab conjugated to a small gold fragment that is specific to Class I
Use an Ab conjugated to a large gold fragment that is specific to Class II
Problems
Very expensive