![]() Dematiaceal & Subcutaneous Mycoses
Dematiaceal & Subcutaneous Mycoses
![]()
Dematiaceae / Chromoblastomycosis / Sclerotic bodies /
Phaeohyphomycosis by W. dermatitidis / Phaeohyphomycosis by E. spinifera /
Cladosporiosis / Eumycotic Mycetoma: black and white grains /
| Dematiaceae: Selected Dematiaceae that are medically important (the dematiaceous pathogens) | ||
 |
 |
|||
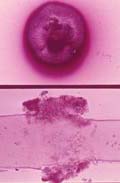
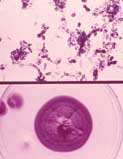
| Piedraia hortae of black piedra | Exophiala werneckii of tinea nigra | |||
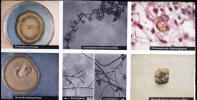 |
 |
|||
| Phialophora verrucosa, Fonsecaea pedrosoi, and F. compacta of chromoblastomycosis | Wangiella/Exophiala dermatitidis of phaeohyphomycosis |
| Chromoblastomycosis: | |||
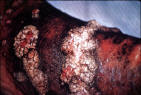 |
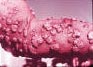 |
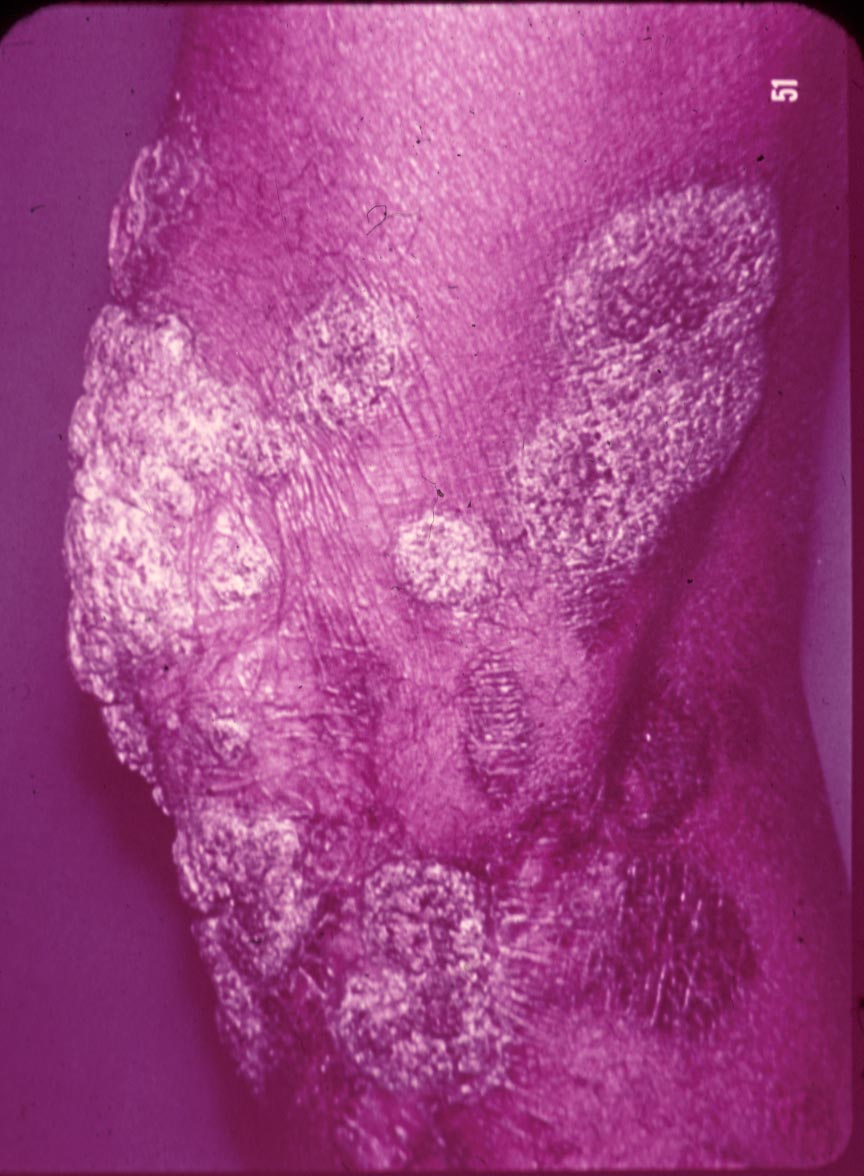 |
||||
| Pedunculated verrucous lesions resembling florets of cauliflower | Pedunculated verrucous lesions resembling florets of cauliflower | Old chronic disease with some scarring and keloid formation. Many lesions were inactive | ||||
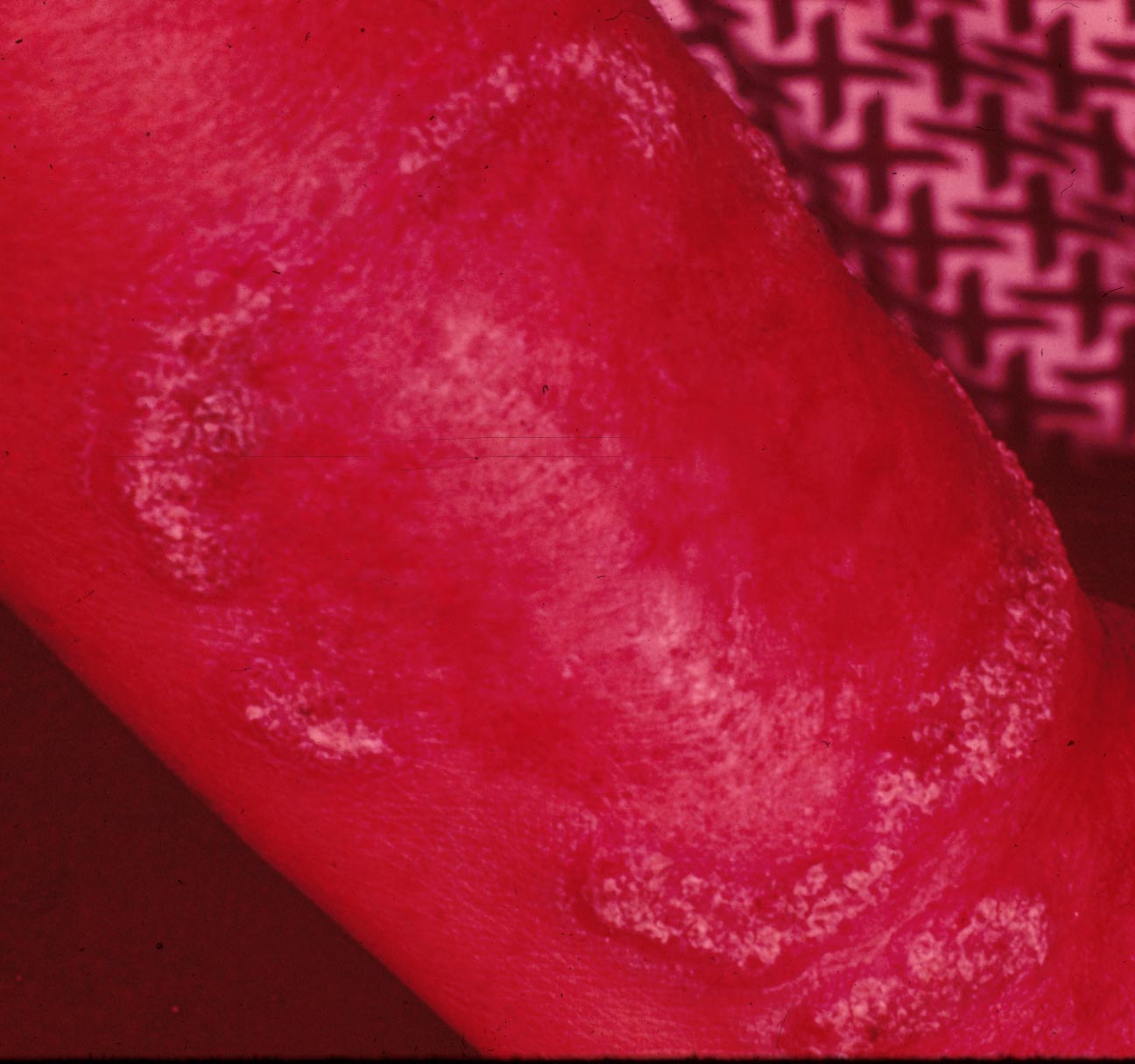 |
 |
 |
||||
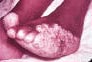
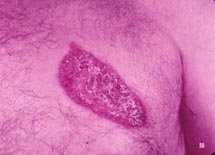
| Active marginal lesion with inactive center | Chronic verrucous infection of foot with secondary infection leading to elephantiasis. | Chest lesion with healing atrophic scarring center and an active raised border is present |
 |
 |
 |
||||
| P. verrucosa | F. pedrosoi | C. corrionii |
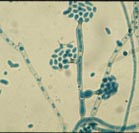 |
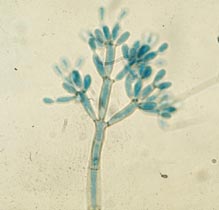 |
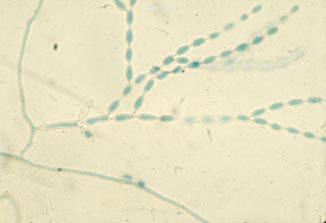 |
||||
| Enteroblastic P. vurrucosa | Holoblastic botryose conidia (sympodulo-conidia) | Holoblastic conidia (catenulate) |
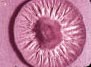
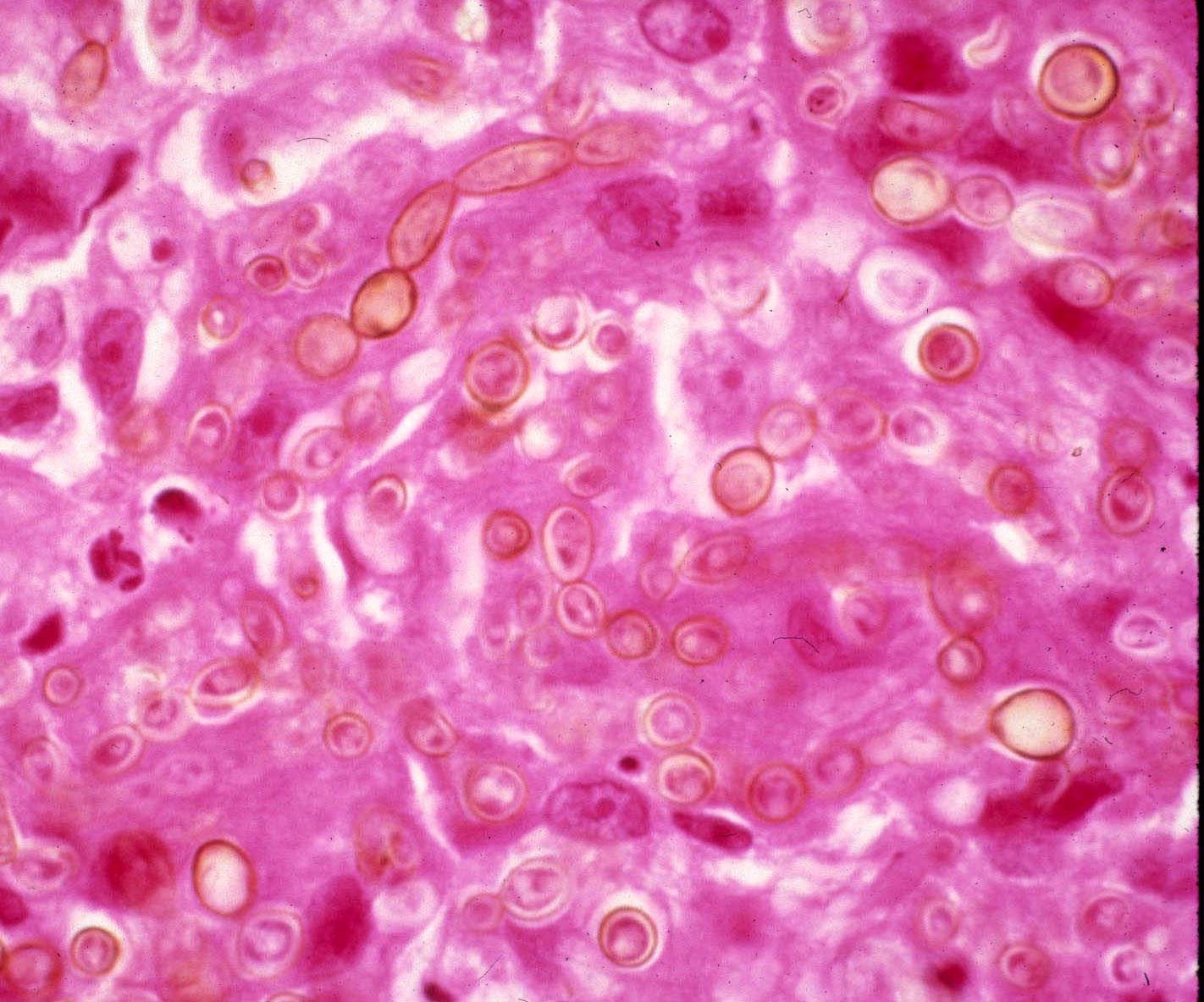
| Sclerotic bodies: of Chromoblastoycosis fungi | |||
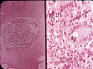 |
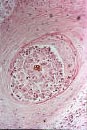 |
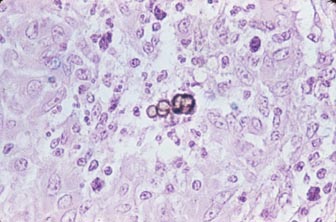 |
||||
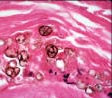 |
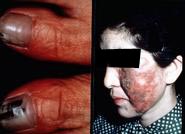
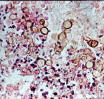
| Phaeohyphomycosis: caused by Wangiella/Exophiala dermatitidis | |||
 |
 |
 |
||||
| Toenail and facial lesions | In vivo phenotypes | Colony on rich medium | ||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
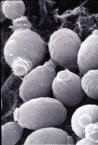
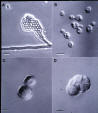
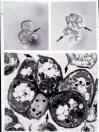
| Scanning of yeast cells | A. hyphae, conrdiophores and conidia, B. normal sized yeasts, C. enlarged yeasts, D. multicellular (sclerotic-like) forms | Multicellular forms exhibiting fissions |
| Phaeohyphomycosis: caused by Exophiala spinifera | |||
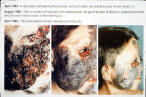 4/1984 8/1984 4/1985 |
 |
|||
| Intraconazol treatment | E. spinifera in vivo |
| Cladosporiosis: | |||
 |
 |
 |
||||
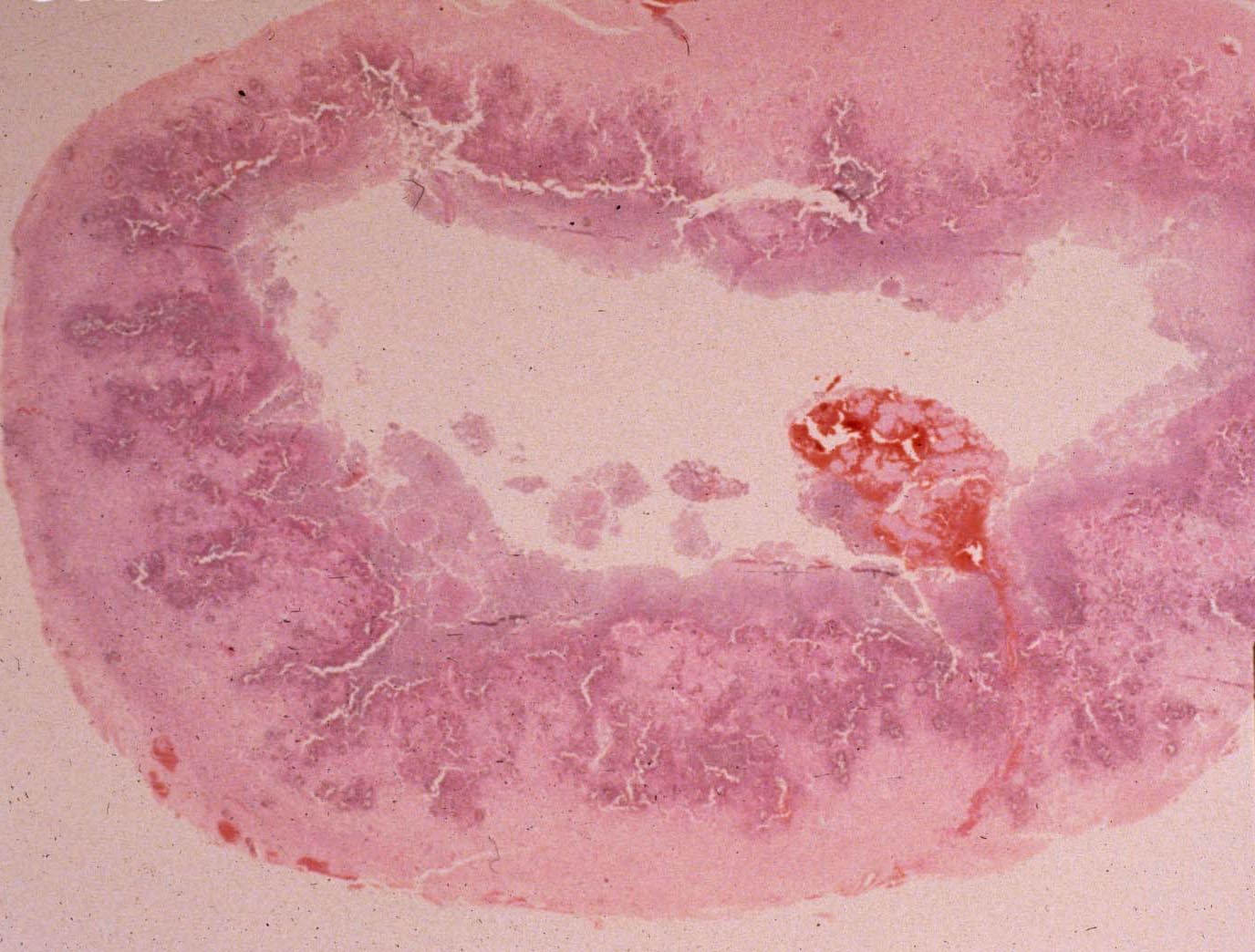
| In vitro blastoconidia | In vivo from lesion aspirate | Cerebral lesion with fungal mass and missing area due to necrosis |
| Eumycotic Mycetoma: Black and white grain | |||
 |
 |
 |
||||
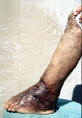
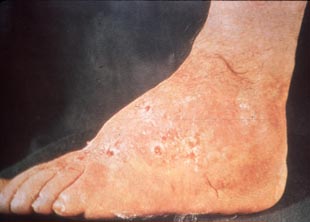
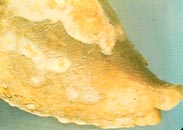
| Madura foot | Madura foot | Madura foot | ||||
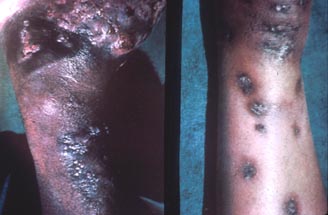 |
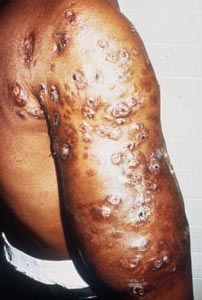 |
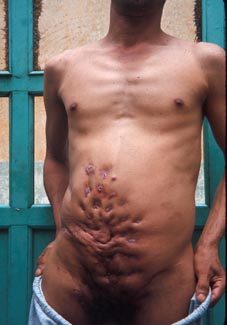 |
||||
| Draining lesions on arms | Draining lesions on arm | Draining lesions on torso | ||||
| Black grains in tissue by dematiaceus fungi: | |||
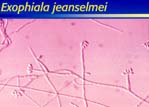 |
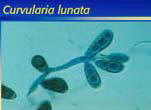 |
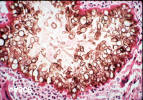 |
||||
| Exophiala jeanselmei | Curvularia lunata | C. geniculata | ||||
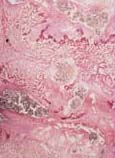 |
||||||
| C. geniculata |
| White grain in tissue and mycotic keratitis by Pseudoallesheria boydii: | |||
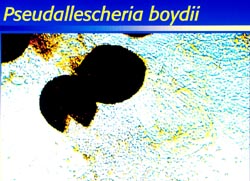 |
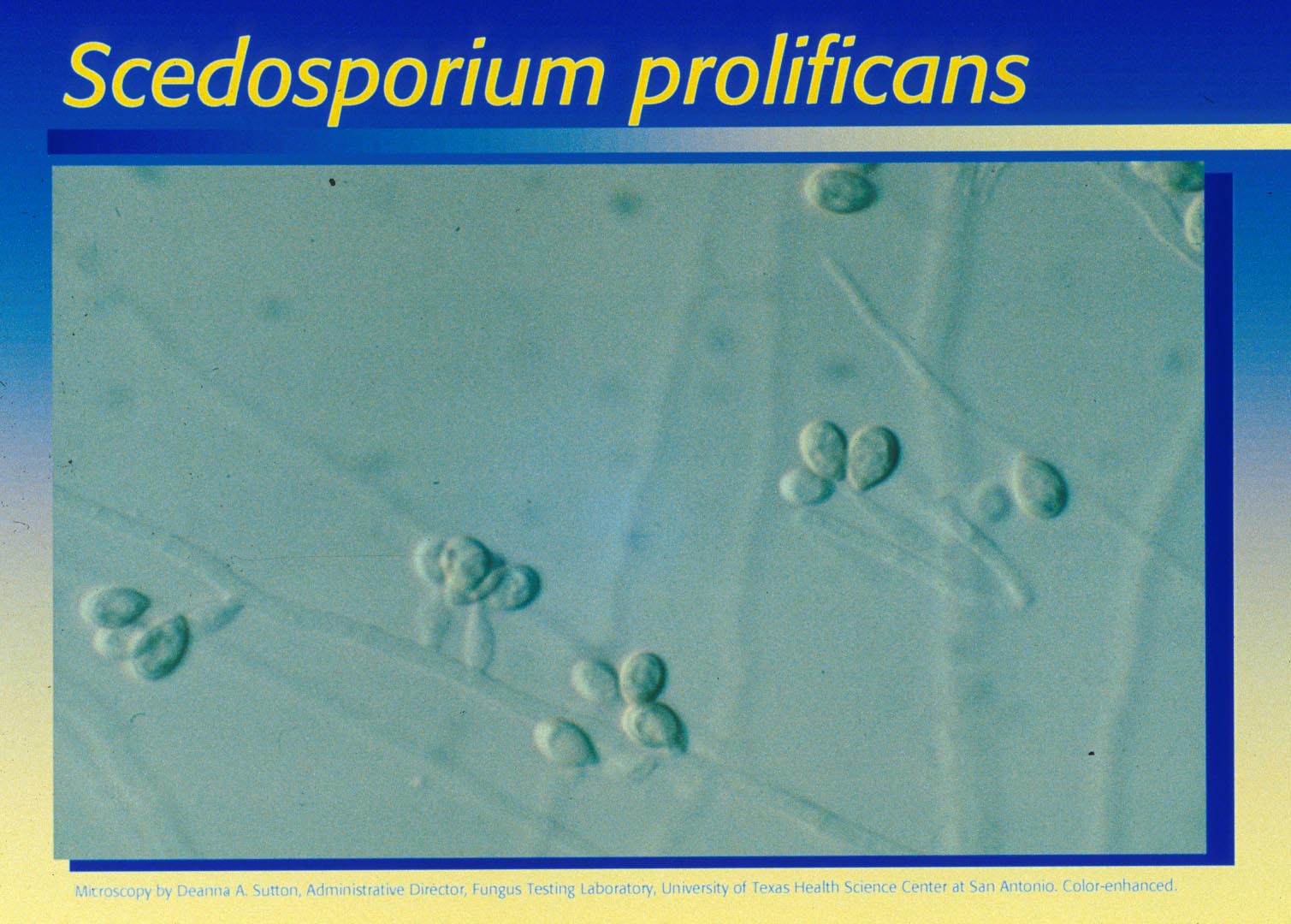 |
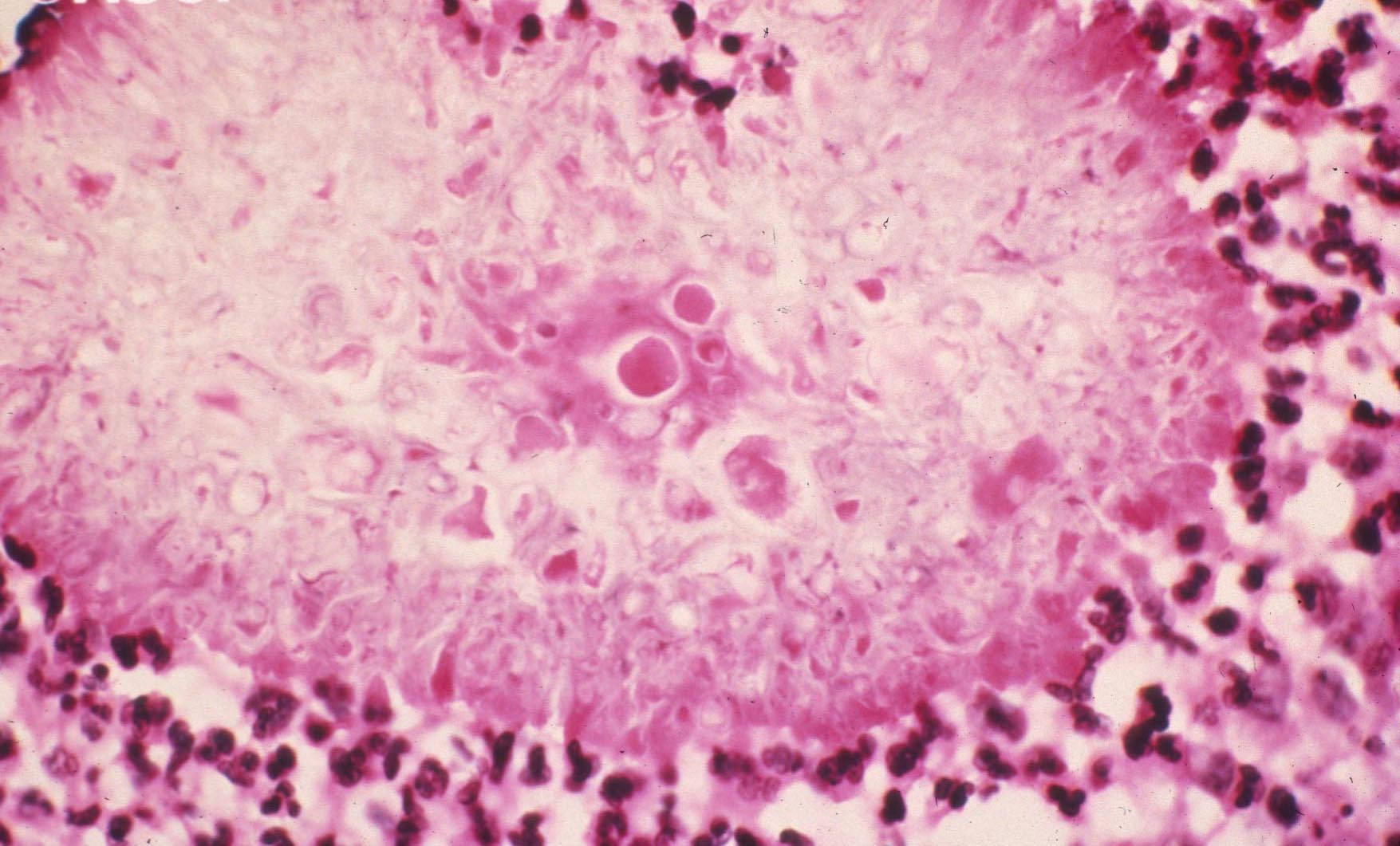 |
||||
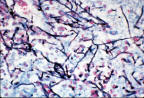
| Pseudallescheria boydii | Scedosporium prolificans | Grains stained by acetocarmine | ||||
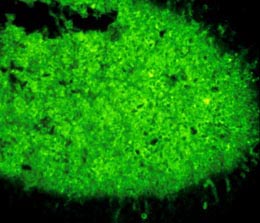 |
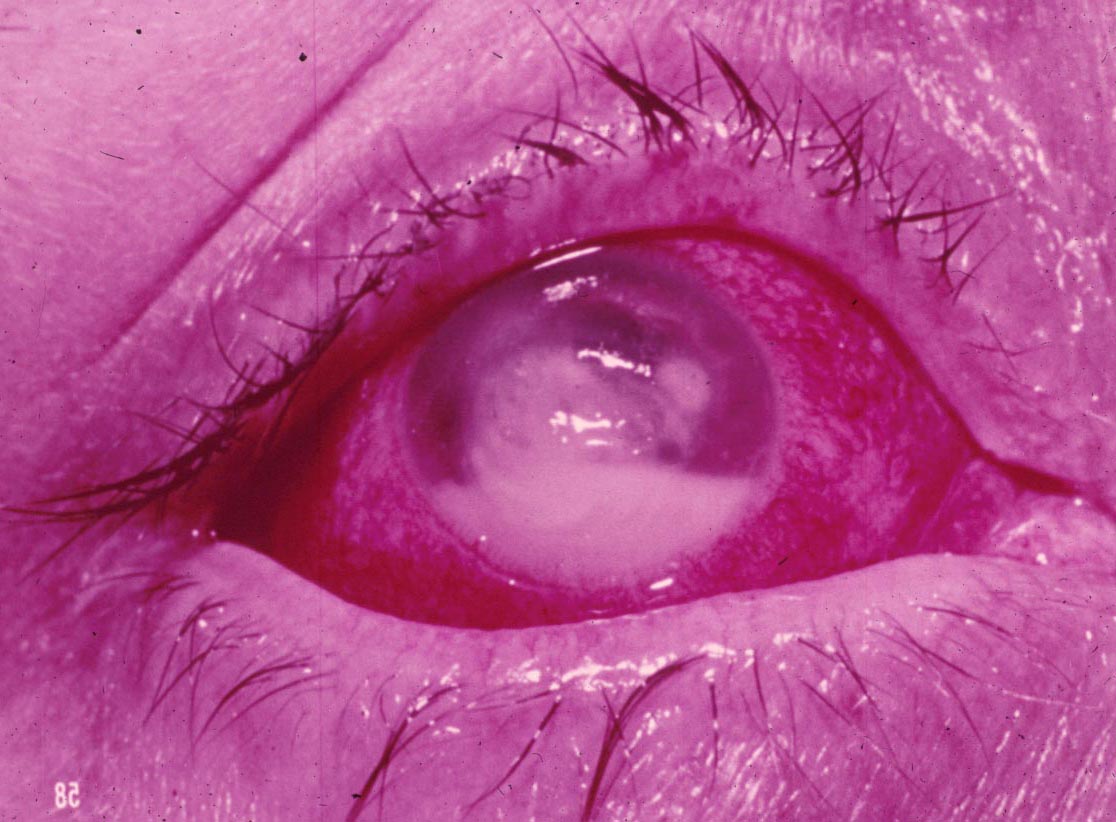 |
 |
||||
| Grains stained by immunofluorecent | Eye infection | Systemic infection | ||||
| Sporotrichosis: By Sporothrix schenckii | |||
| Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis: | |||
 |
 |
 |
||||
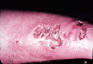
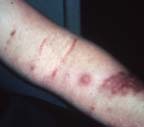
| Initial lesion is discolored, ulcerated and draining, secondary lesions are elevated, but not ulcerated. | Lympho-cutaneous | Non-ulcerating lesions on arm | ||||
 |
||||||
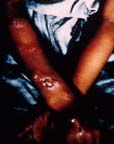
| Gummatous lesions on arm | ||||||
| Cutaneous & subcutaneous sporotrichosis in tissue sections: | |||
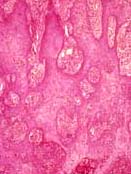 |
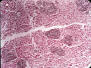 |
 |
||||
| Cutaneous lesions | Numerous small micro abscesses in liver (rare systemic form; hematoxylin and lesion) | Tuberculoid granuloma type lesion. Hematoxylin and eosin stain | ||||
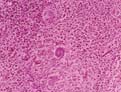 |
||||||
| Giant cells, fibroblasts, and lymphocytes. Hematoxylin and eosin stain | ||||||
| Fixed cutaneous sporotrichosis: | |||
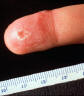 |
 |
 |
||||
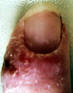
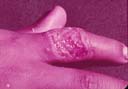
| Laboratory acquired primary lesion | Advanced fixed lesion | Ulcerating fixed lesion and satellite | ||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
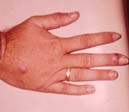
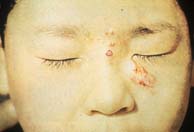
| Finger and satellite "nodule" | Facial lesions and satellites | Facial lesions and culture | ||||
| Sprorthrix schenckii in vivo tissue forms in sporotrichosis: | |||
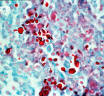 |
 |
|||
| Yeast forms in cutaneous disease | Yeast forms in cutaneous disease | |||
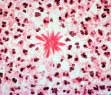 |
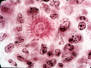 |
|||
| Asteroid bodies in cutaneous disease | Asteroid bodies in cutaneous disease |
| Sporothrix schenckii in vetro: | |||
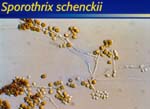 |
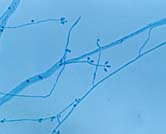 |
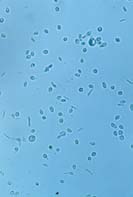 |
||||
| Dematiaceous macroconidia | "Roping" hyphae and holoblastic botryose conidia | Yeast cells at 37°C | ||||
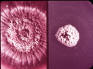 |
||||||
| Left) Folded brown tan mold colony at 25°C; Right) White pasty yeast colony at 37°C | ||||||
|
|
|||||